Hosts on each network can be assigned an IP address manually or dynamically. In a small home network with 2 or 3 computers, we can assign IP addresses manually, but imagine a network with hundreds of computers and you need to assign IP addresses to all of them. This can be a nightmare for network administrators! No two hosts can have the same IP address, and assigning them manually can lead to errors and confusion. Therefore, DHCP service is required to solve this problem. DHCP is needed to simplify the assignment of IP addresses in a network. So, let’s learn a little about DHCP service with this post.
What is the DHCP service?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used to automate the process of configuring devices with IP addresses, thus allowing them to use network services such as DNS. use NTP and any communication protocol based on UDP or TCP. A DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on the network so that it can communicate with other network nodes by IP. DHCP is an evolution of an older protocol called BOOTP.
The DHCP service facilitates the assignment of IP addresses and reduces the work of the network administrator. In addition to the IP address, DHCP also assigns subnets, default gateways, domain name server (DNS) addresses, and other configurations to the host, making the network administrator’s job easier.
DHCP components
DHCP Server: Typically a server or router that holds network configuration information.
DHCP Client: This is a node that receives configuration information from the server like any computer or mobile phone.
DHCP Relay Agent: If you have only one DHCP server for multiple networks, the DHCP Relay Agent on each network forwards the DHCP request to the servers. Because DHCP packets cannot pass through the router. Hence, Relay Agent is needed so that DHCP servers can handle requests from all networks.
IP address pool: contains a list of IP addresses that are available for assignment to the client.
Subnet Mask: It is a 32-bit number that is created by setting Host ID to 0 and Network ID to 1. In this way, the Subnet Mask separates the IP address into network and host addresses.
Lease Time: It is the length of time that the IP address is available to the customer. After this time, the customer must renew the IP address.
Gateway Address: The gateway address tells the host where the Internet connection is.
How does DHCP work?
DHCP works at the application layer of the network to dynamically assign IP addresses to clients through the exchange of a series of messages called DHCP transactions or DHCP conversations.
DHCP discovery: The client sends messages to discover DHCP servers. Client computer sends packet with default broadcast destination 255.255.255.255 or subnet specific broadcast address if configured. 255.255.255.255 is a special broadcast address that means “this network”: it allows you to send a broadcast packet to the network you are connected to, which is called a broadcast.
DHCP Offer: When the DHCP server receives the DHCP Discover message, it offers an IP address to the client by sending a DHCP Offer message. This DHCP offer message includes the IP address offered for the DHCP client, server IP address, client MAC address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, DNS address and lease information.
- Suggested IP address for DHCP client
- Subnet mask to identify the network
- Subnet default gateway IP
- DNS server IP for name translation
DHCP request: In most cases, the client can receive multiple DHCP offers because there are many DHCP servers in the network. If one server’s IP address goes down, other servers can provide backup. But the client accepts only one DHCP offer. In response to this proposal, the client requests the proposed address from one of the DHCP servers by sending a DHCP request. Other IP addresses offered are withdrawn from the remaining DHCP servers and returned to the pool of available IP addresses.
DHCP Confirmation: The server then sends an acknowledgment to the client confirming the DHCP lease to the client. The server may send other configuration that the client may have requested. At this point, the IP configuration is finished and the client can use the new IP settings.
Applications of DHCP service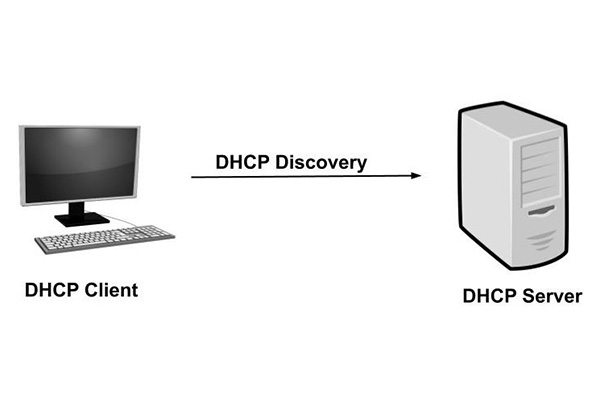
Configuration data sent by the DHCP server and key values
A DHCP server provides configuration data to the requesting client based on the administrator’s policies. Common network parameters (sometimes called “DHCP options”) include subnet mask, router, domain name server, hostname, and domain name.
Since the requesting client does not have an IP address when it joins the network, it broadcasts the request. Therefore, the protocol is used in the early stages of IP communication. If no such dynamic protocol is used to obtain an IP address, the client must use a predefined IP address called a “static IP address” that is manually configured on the client’s network interface in configuration files or with a special configuration command. will be
The DHCP service has three key values:
- Operational tasks are reduced: the network administrator no longer needs to manually configure each client.
- The IP addressing program has been optimized: addresses that are no longer in use are freed up and made available for new clients to connect to.
- User mobility is easily managed: the administrator does not need to manually configure the client when changing the network access point.
DHCP service lease time management
IP address information assigned by DHCP is only valid for a limited time and is known as a DHCP lease. As mentioned, the validity period of each DHCP address is called a lease. When the lease expires, the client can no longer use the IP address and must stop all communication with the IP network unless it wants to renew the lease through the DHCP lease renewal cycle.
To avoid the DHCP server becoming unavailable at the end of the lease term, customers typically start renewing their leases halfway through the lease term. This process ensures robust IP address reassignment to devices. Any device that requests a new IP v.4 (IP version 4 address) upon entering the network and does not receive a response will use the Private Internet Protocol (APIPA) address to select an address.
These addresses are in the network range of 169.254.0.0/16 and replace the DHCP service that serves network nodes in the event of a problem in the network or DHCP not working for a short period of time.
DHCP service usage scenarios
There are four main scenarios for using DHCP:
- Initial connection: The client requests the IP address and other parameter values from the DHCP server to access network services.
- IP Usage Extension: The client contacts the DHCP server to extend the usage of its current IP address.
- IP Usage Extension: The client contacts the DHCP server to extend the usage of its current IP address.
- Client connection after reboot: The client contacts the DHCP server to confirm that it can use the same old IP address before the reboot.
DHCP options
By using DHCP options, you can automatically provide information about the services that the client can use. This is a very efficient way to automate the IP address of time server, mail server, DNS server and printer server. This feature can also be used to provide a file server that is used by the client to initiate a specific boot process, and is primarily used for IP phones and Wi-Fi access points, but can also be used to automatically install client services. to be
Running the DHCP service
The main and comprehensive implementation of DHCP services is provided by the Internet Systems Consortium (ISC). ISC DHCP provides a complete and open source solution for implementing DHCP server and clients and Relay Agent with support for both versions of IP addresses including IPv4 and IPv6. Other DHCP Server products include Microsoft DHCP Server.
The DHCP service can be upgraded with DHCP failover to provide high availability and traffic load balancing. ISC DHCP Failover relies on having a shared server pair. A primary server and a secondary (backup) server. Then a TCP-based communication channel, called a failover channel, must be established between the two servers.
Advantages of DHCP
- It is easy to implement and assign accurate dedicated IP addresses
- No need to manually configure the IP address; Saving time and reducing workload for network administrators
- There are no duplicate or invalid IP assignments and no IP address conflicts
- A big advantage for mobile users; Update new valid configurations automatically when changing network
Disadvantages of DHCP
- Because DHCP servers have no secure mechanism for client authentication, any new client can join the network. This brings security risks such as giving IP addresses to unauthorized clients and leaking IP addresses from unauthorized clients.
- If the network has only one DHCP server, the DHCP server can fail at one point.
- Using the broadcast method and slow service.
last word
In this article, all the important and basic things about the DHCP service were said. We hope this post has helped you learn more about DHCP and its uses. We recommend that you learn more about basic network concepts and essential and basic network services if you are going to set up a DHCP server.









Comment here